- PO Box 77261, Al Quoz Industrial Area 3, Dubai, UAE
- info@ventline.ae

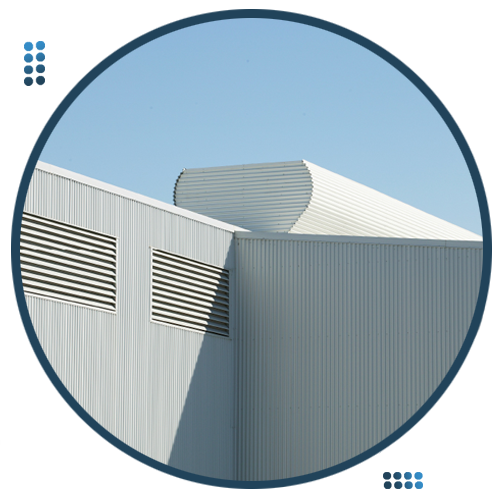
High heat Ventilation is based on the principle that the difference in pressure between the air inlet and exhaust air vents in a building allows natural air exchange to take place. The pressure differences arise due to; a) the buoyancy forces in the building caused by differences in density between the air in the building and the outside air, and the difference in height between the air inlet and exhaust air vents; b) the air currents in the building. Accordingly, the volume of air flowing through the buildings depends on the surplus heat in the building - caused by the convection heat that is emitted into the room air (internal cooling load), the external cooling load (transmission through insolation), wind speed, wind direction, and building geometry.
TYPES OF VENTILATORS
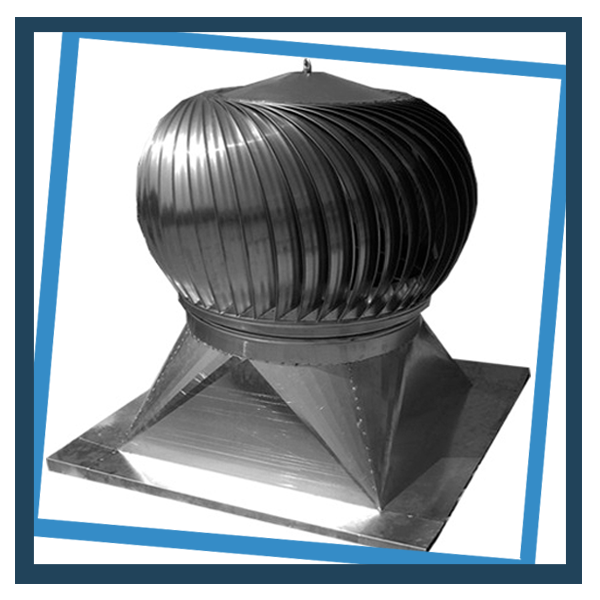
Wind Driven Ventilator
Roof ventilators are naturally powered - by cost-free air. They're an economical ventilation solution suitable for a wide range of applications.
Size and Dimension : Diameter 300mm to 900mm
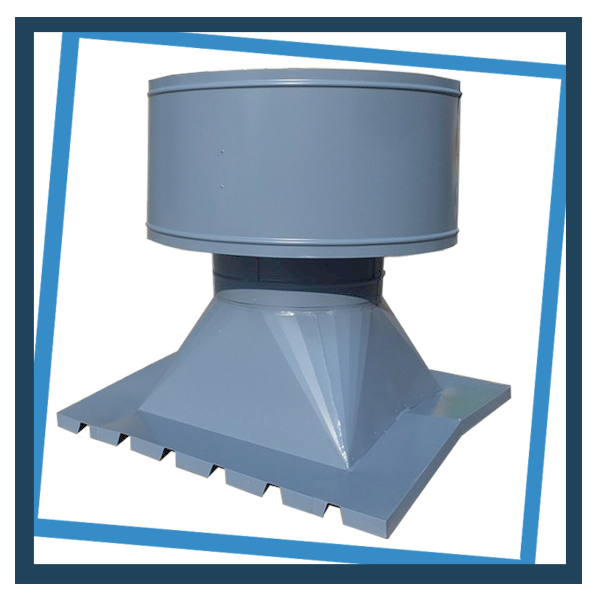
Gravity Ventilator
Stationary roof vents using natural thermodynamic forces that drive air up and through the ventilator ensure that system is directly responsive to internal and external conditions.
Size and Dimension : Diameter 250mm to 1200mm. Height varies
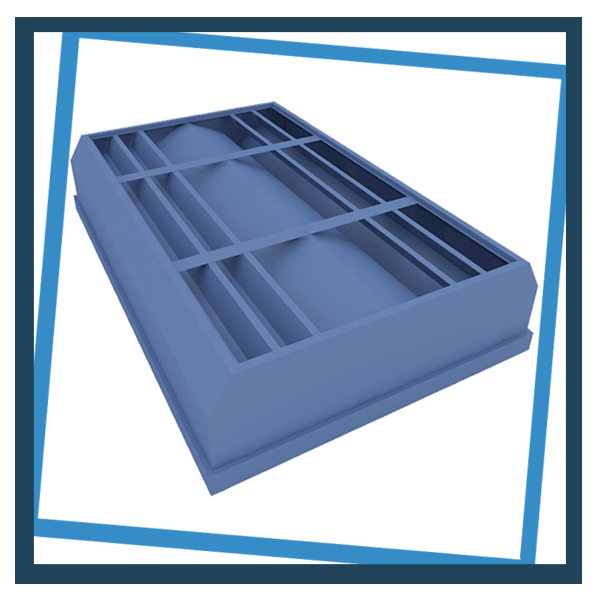
Heat Mover Ventilators
Low-profile ventilators designed for removal of high heat problems for industrial buildings if structural limitations do not allow for heavier ventilators. Coefficient of discharges up to 0.43
Size and Dimension : 1200mm (min) to 3000mm (max) Width. Modular Length 3000mm otherwise, any.
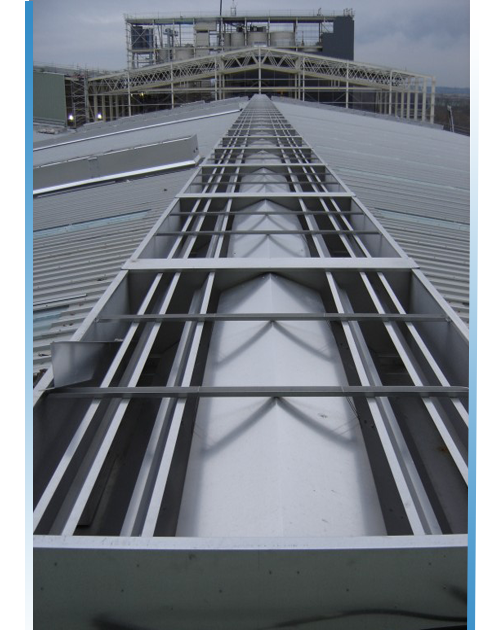
Static Ridge Ventilator
Taking full advantage of natural airflow, the Ventline range of ridge ventilators offer high-performance and cost-effective ventilation solutions for commercial and industrial buildings. Coefficient of discharges up to 0.73
Size and Dimension : Throat size 250mm to 600mm for Crest Ridge Ventilators (CRV) and 700mm to 4500mm for High-Efficiency Ridge Ventilators (HRV). Modular Length 3000mm otherwise, any.
CONFIGURATION & MATERIAL
PERFORMANCE & SELECTION
| Performance and technical characteristics: | contact: +97143419538 or send inquiry to: - info@ventline.ae |
| Selections and sizing | Using Computed Fluid Dynamics (CFD Analysis) for ventilation and temperature. |


